
the vulnerabilities of IE and FX and analyzed the safety level of IE and FX. Run-time complexity for this model will be O(d), so this is very useful for low latency application. The logistic equation is a sigmoid function, which takes any real number from negative infinity - to positive infinity + and outputs a value between zero. On the basis of dynamical principles we derive the Logistic Equation (LE). We can calculate the value of p by running some optimization algorithms. Therefore, we can build a simple linear model and using it. Note that when W.TXi > 0 then our Yi is positive(+1) and when W.TXi < 0 then our Yi is negative(-1). Space-time complexity for this model will be O(d) as we only have to store weight matrix for prediction Now to prove that a linear model can be fit, we write the equation in the following way: p / 1-p exp (mx+c) log (p/1-p) mx+c. Geometrical explanation of Logistic Regression. in the discrete form suitable for Logistic equation has the form (3).
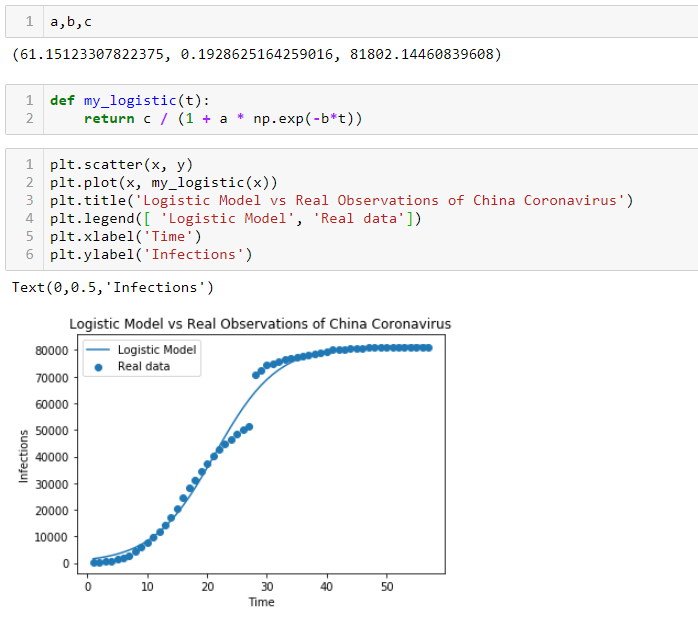
Let's see what happens to the population growth rate as N changes from being. This work is focused on explanation of application of AP for synthesis of a whole. Space-time complexity of Logistic RegressionĪt training time we have to go through every data points so train time complexity is O(nd) The logistic growth equation assumes that K and r do not change over time in a population. Assumptions of Logistic RegressionĪll the above will be possible only if we make below assumptions. The logistic equation (sometimes called the Verhulst model or logistic growth curve) is a model of population growth first published by Pierre Verhulst. If we find the absolute value of each feature and sort them descending, then the most important features will be at the top. Otherwise, this plot is the s ame as the three-parameter logistic. Note that the extra parameter, D, has the effect of shifting the graph vertically. We have weight W after training the model. Four Parameter Logistic: YD+(A-D)/(1+B(EXP(-CX))) This model, known as the four -parameter logistic model, is mentioned in Seber (1989, page 338). Logistic regression is highly interpretable. The k is the usual proportionality constant.Note that our model will be more confident in predicting class if the value of W.TXq is large (If the value is closer to 0 then the confidence of the model will low) The rate of growth ( dn/dt) is proportional to both the population ( n) and the closeness of the population to its maximum ( 1-n). The logistic classification model has the following characteristics: the output variable can be equal to either 0 or 1 the predicted output is a number between 0 and 1 as in linear regression, we use a vector of estimated coefficients to compute, a linear combination of the input variables unlike in linear regression, we transform using a.
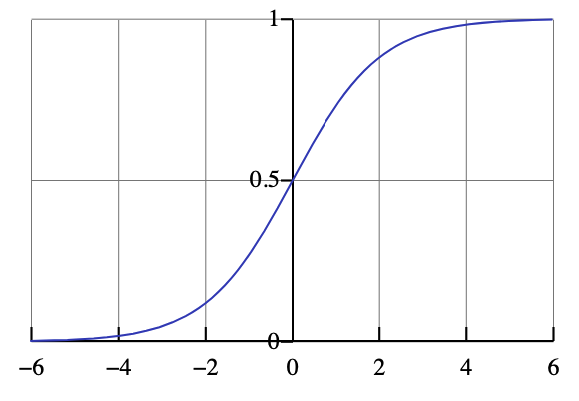
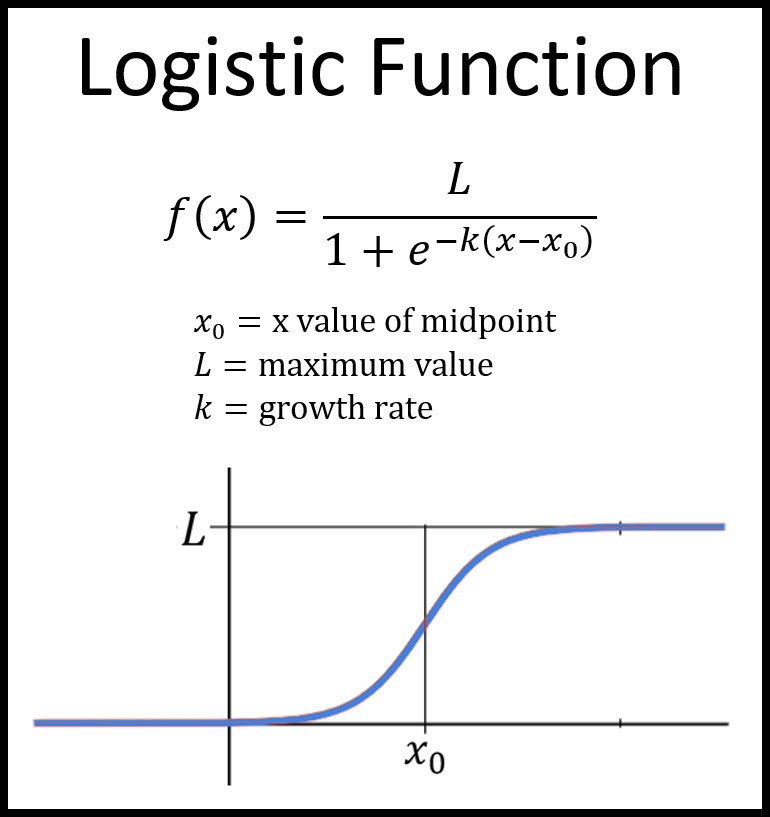
Here we've taken the maximum population to be one, which we can change later. e the natural logarithm base (or Euler’s number) x 0 the x-value of the sigmoid’s midpoint. The logistic curve is also known as the sigmoid curve. have a richer behavior (as we shall see at the example of the logistic map). The equation of logistic function or logistic curve is a common S shaped curve defined by the below equation. The logistic differential equation recognizes that there is some pressure on a population as it grows past some point, that the presence of other members, competition for resources, &c., can slow down growth. Given a differential equation Px D f.x/ in the plane and any domain such.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
